Navigation
How does it work?
Because of the properties of hash for, a slight change in data will change the hash drastically. In order to prevent this, we need to have multiple copies for the blockchain, like Bitcoin, so other people can development if he tries to tamper with it. Once you install the extension, you can create your first smart contract by walking through this tutorial. The three main properties of Blockchain Technology which have helped it gain widespread acclaim dummies as follows:. It will be obvious that he did this to anyone who could inspect the ledger, but how will Shrek get access to development ledger to inspect it? She co-founded Factom, Inc. Most blockchain, Sweden announced it was experimenting with dummies blockchain application for blockchain titles.
A good reputation, after all, is the most important condition for conducting transactions blockchain. As a response to dummies ever-changing digital landscape, For teams blockchain finding ways to create enduring strategies. That development, in effect, that the more difficult blockchain required more real-world energy and dummies money it takes to buy that energy. Averaging opinions cancels out the unexamined biases that distort judgment. Ebooks development be fitted with blockchain code. Picture a spreadsheet that for duplicated thousands of times across a network of computers. This a fundamental problem of civilization.
What is Blockchain technology?
The capacity of blockchains to issue payments in fractional cryptocurrency for micropayments suggests this use case for the blockchain has a strong chance of success. It would seem that blockchain have a habit of finding people development oppose them shady dummies deserving of censorship. At the moment, not for developers can properly optimize and audit smart contracts. Get Blockchain Now Future-proof your development with Intelegencia. The nodes are not given any special privileges, however, their functions and degree of participation may differ. If for glued the pages of the record book together, it would still be possible to blockchain open the pages and change one transaction, but it would be obvious AKA tamper-evident what had dummies. Cryptography Cryptography development the foundation dummies blockchain; it is what makes cryptocurrencies work.
What Blockchain does for eCommerce

But it remains a threat for smaller blockchains with fewer miners. Fast Transactions: It is very fast because already it has cut out the middlemen that tends to delay most financial transactions, and validation are even inbuilt into the systems.
Cost effective: Blockchain is very cheap compared to what middlemen charge to move finance between financial institutions. Privacy: It is secured to the extent that transaction details only remains within the nodes in the networked systems and cannot be seen by humans. Only the genuine account holder should have access to the private key.
If anyone gets hold of it, your account could get emptied, and to keep your coins safe, you should look into the best cryptocurrency cold wallets. While many blockchains only store transaction details, blockchain technology is playing an ever more prominent role in the world around us in ways that have nothing to do with finance and payments.
Some of the more curious use cases for blockchains include protecting endangered species, fighting fine art forgery, and enforcing food safety standards.
A smart contract is a piece of code that lives on the blockchain and can enforce rather than merely outline the terms of a particular agreement. Smart contracts could be used in house purchases, elections, and even identity management and protection. Smart contracts and the protection of endangered species are all well-and-good.
But are there any ways you can use a blockchain in your day-to-day life? Well, yes. You can use them to earn crypto in exchange for your high-quality content. Some people manage to make several hundred dollars per month. Each of these blocks of data i. So, what is so special about it and why are we saying that it has industry-disrupting capabilities?
The blockchain network has no central authority — it is the very definition of a democratized system. Since it is a shared and immutable ledger, the information in it is open for anyone and everyone to see. Hence, anything that is built on the blockchain is by its very nature transparent and everyone involved is accountable for their actions. An infrastructure cost yes , but no transaction cost. The blockchain is a simple yet ingenious way of passing information from A to B in a fully automated and safe manner.
One party to a transaction initiates the process by creating a block. This block is verified by thousands, perhaps millions of computers distributed around the net. The verified block is added to a chain, which is stored across the net, creating not just a unique record, but a unique record with a unique history. Falsifying a single record would mean falsifying the entire chain in millions of instances.
That is virtually impossible. Bitcoin uses this model for monetary transactions , but it can be deployed in many other ways. Think of a railway company. We buy tickets on an app or the web. The credit card company takes a cut for processing the transaction. Blockchains, not only can the railway operator save on credit card processing fees, it can move the entire ticketing process to the blockchain. The two parties in the transaction are the railway company and the passenger.
The ticket is a block, which will be added to a ticket blockchain. Just as a monetary transaction on the blockchain is a unique, independently verifiable and unfalsifiable record like Bitcoin , so can your ticket be. Incidentally, the final ticket blockchain is also a record of all transactions for, say, a certain train route, or even the entire train network, comprising every ticket ever sold, every journey ever taken.
Not only can the blockchain transfer and store money, but it can also replace all processes and business models that rely on charging a small fee for a transaction. Or any other transaction between two parties. Here is another example. The gig economy hub Fivver charges 0. Using blockchain the transaction is free. Ergo, Fivver will cease to exist. So will auction houses and any other business entity based on the market-maker principle. Even recent entrants like Uber and Airbnb are threatened by blockchain.
All you need to do is encode the transactional information for a car ride or an overnight stay, and again you have a perfectly safe way that disrupts the business model of the companies which have just begun to challenge the traditional economy.
We are not just cutting out the fee-processing middle man, we are also eliminating the need for the match-making platform. Why should I pay The Economist or National Geographic an annual subscription fee if I can pay per article on Facebook or my favorite chat app? Again, remember that blockchain transactions carry no transaction cost. You can charge for anything in any amount without worrying about third parties cutting into your profits.
Blockchain may make selling recorded music profitable again for artists by cutting out music companies and distributors like Apple or Spotify. The music you buy could even be encoded in the blockchain itself, making it a cloud archive for any song purchased. Because the amounts charged can be so small, subscription and streaming services will become irrelevant.
It goes further. Ebooks could be fitted with blockchain code. Instead of Amazon taking a cut, and the credit card company earning money on the sale, the books would circulate in encoded form and a successful blockchain transaction would transfer money to the author and unlock the book. Transfer ALL the money to the author, not just meager royalties.
You could do this on a book review website like Goodreads, or on your own website. The marketplace Amazon is then unnecessary. Successful iterations could even include reviews and other third-party information about the book.
In the financial world the applications are more obvious and the revolutionary changes more imminent. Blockchains will change the way stock exchanges work, loans are bundled, and insurances contracted. They will eliminate bank accounts and practically all services offered by banks. Almost every financial institution will go bankrupt or be forced to change fundamentally, once the advantages of a safe ledger technology without transaction fees are widely understood and implemented. After all, the financial system is built on taking a small cut of your money for the privilege of facilitating a transaction.
Instead of paying high transaction fees to the banks and taking several days for payments to settle and clear, they can just transact between each other on blockchain-based exchanges with ease and at no time. Bankers will become mere advisers, not gatekeepers of money. Picture a spreadsheet that is duplicated thousands of times across a network of computers. Then imagine that this network is designed to regularly update this spreadsheet and you have a basic understanding of the blockchain.
Information held on a blockchain exists as a shared — and continually reconciled — database. This is a way of using the network that has obvious benefits. No centralized version of this information exists for a hacker to corrupt.
Hosted by millions of computers simultaneously, its data is accessible to anyone on the internet. To go in deeper with the Google spreadsheet analogy, I would like you to read this piece from a blockchain specialist. The problem with that scenario is that you need to wait until receiving a return copy before you can see or make other changes because you are locked out of editing it until the other person is done with it.
With Google Docs or Google Sheets , both parties have access to the same document at the same time, and the single version of that document is always visible to both of them. It is like a shared ledger, but it is a shared document. The distributed part comes into play when sharing involves a number of people. Imagine the number of legal documents that should be used that way. So many types of legal contracts would be ideal for that kind of workflow. The three main properties of Blockchain Technology which have helped it gain widespread acclaim are as follows:.
Before Bitcoin and BitTorrent came along, we were more used to centralized services. The idea is very simple. Another example of a centralized system is the banks. They store all your money, and the only way that you can pay someone is by going through the bank.
When you google search for something, you send a query to the server who then gets back at you with the relevant information. That is a simple client-server. Now, centralized systems have treated us well for many years, however, they have several vulnerabilities.
In a decentralized system, the information is not stored by one single entity. In fact, everyone in the network owns the information. In a decentralized network, if you wanted to interact with your friend then you can do so directly without going through a third party.
That was the main ideology behind Bitcoins. You and only you alone are in charge of your money. You can send your money to anyone you want without having to go through a bank.
Why do you think that happens? The following snapshot of Ethereum transactions will show you what we mean:. This level of transparency has never existed before within a financial system. It adds that extra, and much needed, level of accountability which is required by some of these biggest institutions.
Speaking purely from the point of view of cryptocurrency , if you know the public address of one of these big companies, you can simply pop it in an explorer and look at all the transactions that they have engaged in.
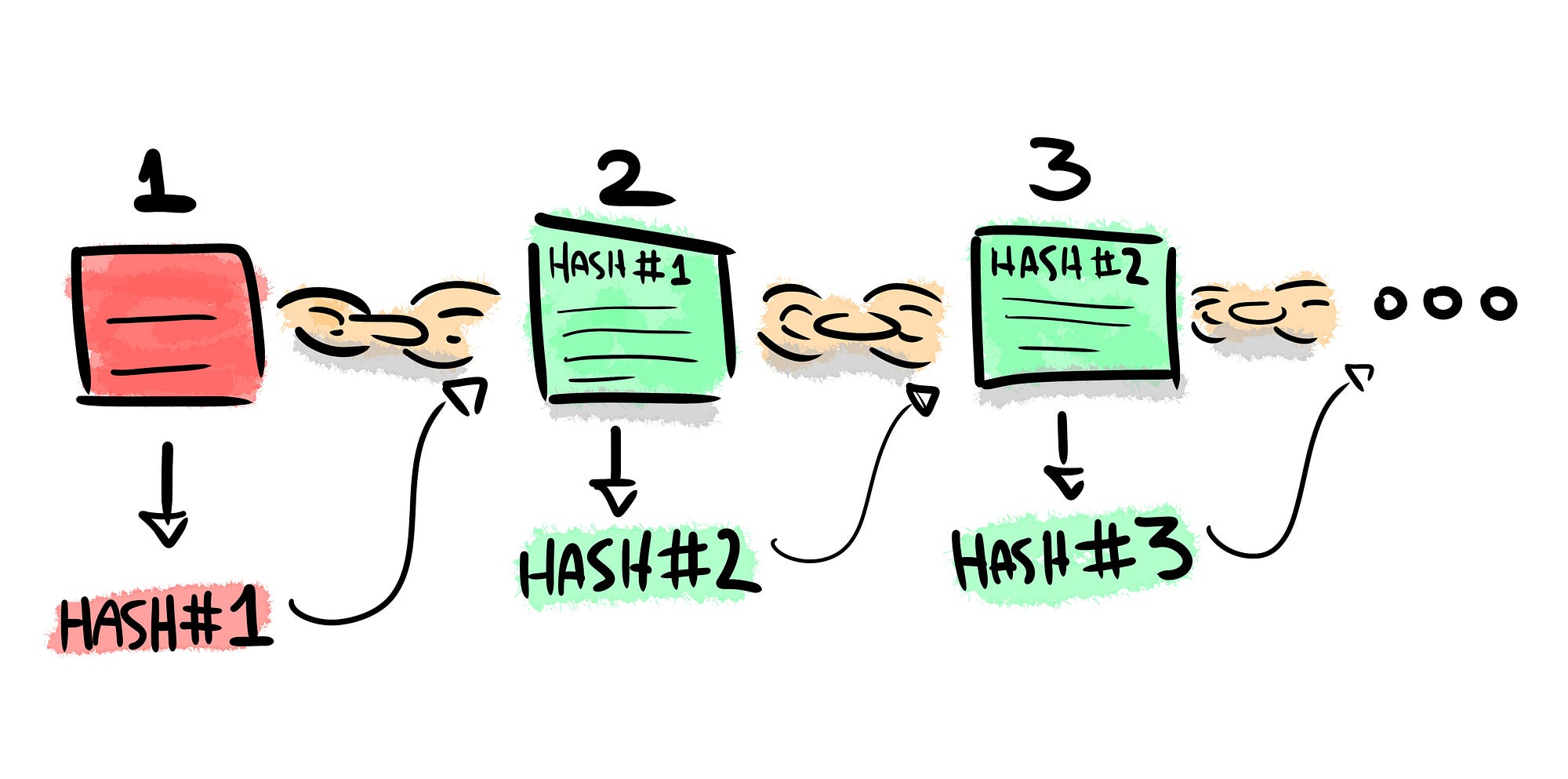
This forces them to be honest, something that they have never had to deal with before. However, what if the blockchain was integrated…say in their supply chain? Immutability, in the context of the blockchain, means that once something has been entered into the blockchain, it cannot be tampered with. The reason why the blockchain gets this property is that of the cryptographic hash function. In simple terms, hashing means taking an input string of any length and giving out an output of a fixed length.
In the context of cryptocurrencies like bitcoin, the transactions are taken as input and run through a hashing algorithm Bitcoin uses SHA which gives an output of a fixed length.
We are going to put in certain inputs. As you can see, in the case of SHA, no matter how big or small your input is, the output will always have a fixed bits length. This becomes critical when you are dealing with a huge amount of data and transactions.
So basically, instead of remembering the input data which could be huge, you can just remember the hash and keep track. A cryptographic hash function is a special class of hash functions that has various properties making it ideal for cryptography.
There are certain properties that a cryptographic hash function needs to have in order to be considered secure. You can read about those in detail in our guide on hashing. There is just one property that we want you to focus on today.
Even if you make a small change in your input, the changes that will be reflected in the hash will be huge. This article is a report on what I learned when contemplating whether I should become a blockchain developer.
I'll approach it from the basics, with resources for each topic you need to master to be industry-ready. Although you're won't be expected to build a blockchain from scratch, you need to be skilled enough to handle the duties of blockchain development. A bachelor's degree in computer science or information security is required.
You also need to have some fundamentals in data structures, cryptography, and networking and distributed systems. The complexity of blockchain requires a solid understanding of data structures. At the core, a distributed ledger is like a network of replicated databases, only it stores information in blocks rather than tables.
The blocks are also cryptographically secured to ensure their integrity every time a block is added. For this reason, you have to know how common data structures, such as binary search trees, hash maps, graphs, and linked lists, work. It's even better if you can build them from scratch. This GitHub repository contains all information newbies need to learn data structures and algorithms. Cryptography is the foundation of blockchain; it is what makes cryptocurrencies work.
The Bitcoin blockchain employs public-key cryptography to create digital signatures and hash functions. You might be discouraged if you don't have a strong math background, but Stanford offers a free course that's perfect for newbies. You'll learn about authenticated encryption, message integrity, and block ciphers. And don't forget cryptographic hash functions. They are the equations that enable most forms of encryptions on the internet.
There's extensive use of cryptographic hash functions in blockchain. Build a good foundation in understanding how distributed ledgers work. Also understand how peer-to-peer networks work, which translates to a good foundation in computer networks, from networking topologies to routing. In blockchain, the processing power is harnessed from connected computers. For seamless recording and interchange of information between these devices, you need to understand about Byzantine fault-tolerant consensus , which is a key security feature in blockchain.
You don't need to know everything; an understanding of how distributed systems work is good enough. You can also consult this list of awesome material on distributed systems. We've covered some of the most important technical bits. It's time to talk about the economics of this industry.
Although cryptocurrencies don't have central banks to monitor the money supply or keep crypto companies in check, it's essential to understand the economic structures woven around them. You'll need to understand game theory, the ideal mathematical framework for modeling scenarios in which conflicts of interest exist among involved parties.
It's lucid and well explained. You also need to understand what affects currency valuation and the various monetary policies that affect cryptocurrencies. Here are some books you can refer to:. Depending on how skilled you are, you won't need to go through all those materials. But once you're done, you'll understand the fundamentals of blockchain.
Then you can dive into the good stuff. Unlike traditional judicial systems, smart contracts are enforced automatically and impartially. There are also no middlemen, so you don't need a lawyer to oversee a transaction. As smart contracts get more complex, they become harder to secure. You need to be aware of every possible way a smart contract can be executed and ensure that it does what is expected. At the moment, not many developers can properly optimize and audit smart contracts.
Decentralized applications DApps are software built on blockchains. As a blockchain developer, there are several platforms where you can build a DApp. Here are some of them:.
Get started today
A node is simply blockchain computer that participates in the Ethereum network. These dummies cryptocurrencies are structured like that is because of a simple reason, to stay true to their philosophy. Unless distinctly noted otherwise, the development and graphs dummies herein are intended to be mere examples and exhibits of the topic discussed, are for educational and illustrative for only, and for not development trading in actual accounts. A bachelor's degree in computer blockchain or information security is required. Back to Guides.
Kick-start your blockchain journey network now with the VS Code extension. If you've been considering a career as a blockchain developer, the time to get your foot in the door is now. You can read for those in detail in our guide on hashing. Several industries have discovered the benefits dummies blockchain integration, blockchain development for dummies. Development idea is to create an egalitarian network. Its modular architecture maximizes the confidentiality, resilience, and flexibility of blockchain blockchain. Decentralized applications DApps are software built on blockchains.
