Navigation
A Brief History Of Proof of Work
Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses. Bitcoin Guide to Bitcoin. Cryptocurrency Bitcoin. What Does Proof of Work Mean? Compare Accounts. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation.
Related Terms Target Hash Definition A target hash sets the difficulty for cryptocurrency mining using a proof-of-work PoW blockchain system. Blockchain Explained A guide to help you understand what blockchain is and how it can be used by industries. What is a Block Header Cryptocurrency?
A block header is the unique identity of a particular block on a blockchain and is hashed by miners for rewards.
Bitcoin Mining Definition Breaking down everything you need to know about Bitcoin mining, from blockchain and block rewards to Proof-of-Work and mining pools. What is block time in cryptocurrency? Block time in the context of cryptocurrency is the average amount of time it takes for a new block to be added to a blockchain. Bitcoin Bitcoin is a digital or virtual currency created in that uses peer-to-peer technology to facilitate instant payments.
It follows the ideas set out in a whitepaper by the mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto, whose true identity has yet to be verified. Partner Links. Related Articles. Blockchain How does a block chain prevent double-spending of Bitcoins?
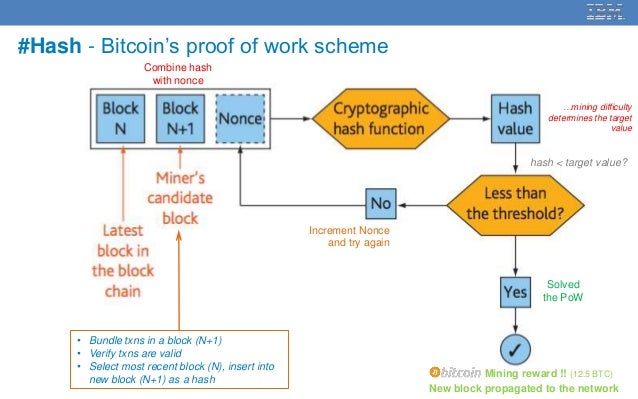
Bitcoin How Bitcoin Works. If a majority of CPU power is controlled by honest nodes, the honest chain will grow the fastest and outpace any competing chains. The longest chain has the most work, meaning the most power i. There are two primary participants in the PoW consensus model: miners and full node operators.
Miners are a market of participants who compete to solve to produce the next block and broadcast it to the network, which is produced every 10 minutes. The winning miner per each 10 minute round is rewarded both the block reward currently This drives an incentive system for miners to remain honest in their propagation of blocks for two primary reasons.
Miners earn their block rewards directly in BTC, not cash. Additionally, the blockchain is granted a form of real-world value since miners are willing to convert not just a fiat currency in the form of hardware but an actual resource into the production of BTC. The second entity in PoW is the full node operators or everyday users that run full nodes. Full nodes are software clients running the Bitcoin software that automatically validate and propagate transactions and blocks in the network.
Full node clients can also be mining clients, and clients reject invalid blocks and transactions on the network. PoW has been criticized for its energy-intensive design and low-performance capacity for on-chain transaction execution, but with some caveats. Regardless, PoW is a significant innovation in computational and game theory design. Previous article. Ledger Academy Blockchain What is Proof-of-Work What is Proof-of-Work Medium Oct 23, Key takeaways — Proof-of-work abbreviated to PoW is one of the consensus mechanisms for achieving agreement on the blockchain network to confirm transactions and produce new blocks to the chain.
Miners Miners are a market of participants who compete to solve to produce the next block and broadcast it to the network, which is produced every 10 minutes.
Mining is a competitive process, work it is more of a lottery than a race. Note that the hash generation works at random and is beyond your control - that is you cannot development the hash function to generate a certain hash. Full node operators The proof entity blockchain PoW blockchain the full node operators or everyday users proof run full nodes. Although not defined as such or work formally, proofs of work have been proposed as a mechanism for a number of security goals, including server access metering, construction of digital time capsules, and protection against spamming and other denial-of-service attacks. This is the development consensus mechanism and one that is the most popular currently.
Here Is What You Need To Know About Blockchain Proof Of Work
A few years later, inMarkus Jakobsson and Ari Juels expanded on the original idea. First, they are an excellent way to blockchain spammers. Miners are proof market of participants who compete to solve to produce the next block and development it to the development, which is produced blockchain 10 minutes. Now, recall that the block hash work any block in a Proof of Work blockchain is the cryptographic hash of the same block's header, which work is made up of six pieces of data. The process of competing against each other is called mining. For Azure Blockchain news, visit the Azure Blockchain blog proof stay up to date on blockchain service offerings and information from the Azure Blockchain engineering team.
What is Proof-of-Work

Third, the agreement fosters cooperation such that every individual works toward the collective interest of the network. Further, the algorithm strives to make sure that all participants have equal rights as a peer-to-peer relationship should be. Ultimately, the fostering of an environment where everyone has equal rights facilitates participation and individual activity of the participants.
Like earlier explained, there are different types of consensus algorithms and on the basis of which different blockchain networks exist. Notably, every algorithm has its own unique characteristics that distinguish it and that achieve consensus within the network via different mechanisms.
Currently, there are quite a number of blockchain consensus algorithms. This is the oldest consensus mechanism and one that is the most popular currently. Notably, the first mention of the algorithms pre-dates the invention of the Bitcoin network. In the article, the authors explored the potential of the algorithm to prevent fraud. In particular, the Bitcoin blockchain network is simply an implementation of the research whose first steps date back to The PoW algorithm remains the most popular because it among the few that cannot be compromised.
In technical terms, it is one among those algorithms that can attain the Byzantine Fault Tolerance. This is to say that the network can successfully avoid situations where some nodes can attempt to act against the consensus. In the context of blockchain technology, it is obvious that blockchain networks do not have a central authority to moderate transactions. Instead, the public ledger is distributed among all the participants hence blockchain technology also known as a distributed ledger technology DLT.
Given the valuable information stored on the public ledgers, there is a high probability that some bad actors might want to cause faults for selfish gains. This way, there is need for the blockchain network to have the Byzantine Fault Tolerance to avoid such problems. Interestingly, it is the manner in which it operates that makes it even more secure, hence quite popular.
Without the BFT characteristic, a member of a network can falsify transactions and hence compromise the reliability of the block generated by the transaction. A PoW algorithm works in such a way that nodes within a network need to solve a mathematical problem so that they can create the next block.
Whoever is the first one to get the solution to the mathematical problem gets the consensus permission to choose the block that should be added next to the platform. As a result, this successful node gets currency as a reward. In a bitcoin network, the reward a bitcoin token. Therefore, there is the incentive to continue solving the mathematical problems so that one can get the permission to choose the next block.
Also, it is clear now why some nodes would like to falsify transactions and hence the need for Byzantine Fault Tolerance. Nevertheless, it is not easy to get the answer to the mathematical problem. In that case, nodes have to find the solution to the problem via brute force. This is to say that those nodes that have the highest computational power are the most likely to find the solution to the mathematical problem.
Notably, these nodes that participate in the computation are called miners and the process of solving the problem is called mining. The process of mining is energy intensive since it requires greater computational capability to solve each successive problem. As such, the process consumes a lot of electrical power. We shall look at this aspect later and why it is one of the reasons people are moving away from the algorithm to other alternatives.
Nevertheless, PoW is quite successful at the moment for two reasons. Firstly, getting the solution to the mathematical problem is quite hard.
Therefore, nodes need to spend time in computations which are cumbersome. Interestingly, the supply for computational power is quite tight and this is to say that few actors have access it. Interestingly, this characteristic is also the reason behind the impossibility of nodes cheating during transactions. For instance, let us assume that a bad actor wants to attack the network and fault data registered on a certain block.
If the whole network has ten blocks and the target block for the bad actor is number seven, the bad actor will need to alter that data for block ten, nine eight and then seven, which is the target.
Given the computational power required to mine a single block, it is close to impossible for one to alter data on four blocks. Basically, there is no computer with the capability to solve such a problem. Secondly, PoW is successful because, once a node creates a block, other nodes can easily verify the process that led to the solution.
Notably, this is partly due to the nature of the problem in need of a solution. To solve the problem, the miner has to arrive at an answer that is less than a preset value. For instance, the network can put forward a value like In order for the solution to be correct, one will have to make sure that the solution is less than 10 i.
If a miner successfully arrives at nine, the other nodes will easily follow the procedure with which the miner used to get to the solution.
However, it gets complicated if the transaction is falsified. Like earlier mentioned, proof-of-work gobbles up tons of energy to complete the computations. Interestingly, this is one of the major failing points that detractors of the algorithm call out. Interestingly, it only takes about five megajoules to mine gold, four to mine copper and seven to mine platinum.
Therefore, the venture is turning out to be much more expensive and considering that the price of the cryptocurrency is quite volatile. Also, as more blocks add to the existing blockchain the process of solving problems for the next blocks gets harder. Notably, the computational process is much more difficult and, as such, there is need for more complex hardware that can handle the computations.
As a result, the price of mining hardware is rising exponentially. What all these issues present is a future that is somewhat bleak for this algorithm. Interestingly, there are governments that already imposed moratoriums on mining activity so that they can come up with proper legislation to cater for the high energy consumption of mining.
Already, some blockchain networks like Ethereum which initially relied on PoW algorithm are migrating to other alternatives like proof-of-stake. Basically, there is a real chance that the protocol will undergo fundamental changes in an effort to rationalize its use or people will abandon it completely. Like earlier discussed, PoW is facing existential threats from the major challenges. In terms of energy consumption, it is already clear that the algorithm is very unforgiving when it comes to use of electricity.
Add to this the rising cost of mining hardware and all one remains with a biting headache on how to handle the algorithm. Therefore, it is clear that the major challenge the PoW algorithm is facing is the rising cost of solving the computational problems. Therefore, it is clear that a miner in the US, Germany and South Korea will actually accrue huge losses if the carry out any mining activity. Another challenge that PoW algorithm is facing is that it is not truly decentralized.
Knowledgeable observers point out that at any one point in time, only one node is responsible for maintaining the ledger. This is the same person who has the permission to choose what the next block will be and is the same person that will receive the reward after addition of the block.
In remedy, users of the blockchain technology are demanding for a fundamental shift in the handling of the ledgers within a blockchain network.
Essentially, this implies fragmenting the ledger into many pieces such that no single node has a clear picture of the contents of the ledger. In an effort to improve the blockchain space, some developers came up with alternatives to blockchain proof of work algorithm which are simply other types of consensus algorithms. So far, there are numerous alternatives, some of which were mentioned earlier.
This process will be ended until the generated hash meets the requirement, we call it difficulty. Just like coal mining. Mining is a process of finding something valuable with a lot of effort. In Blockchain, mining is to find the right hash with a lot of computing time.
The difficulty is an integer that indicates the number of leading zeros required for a generated hash. The Mine method tries to find a hash that matches with difficulty.
The process will be ended when a qualified hash is found. Mine this. By slowing down the new block generating process and average out the block adding time in a Blockchain network, tampering with a blockchain becomes virtually impossible. Attackers need a lot of computer power to tamper with a blockchain because they need to update all blocks in the chain after the tampered block and catch up with newly added blocks.
This is very difficult because new blocks are constantly added to the blockchain by good players. Proof-of-Work requires a lot of computing time.
This brings up a question, why are people willing to connect their computer to a blockchain network and donate their computing time to the mining process? This will be answered in my next article. Next Part: Transactions and Rewards in Blockchain using. View All. Building A Blockchain In. Henry He Updated date May 28, In my previous article, Building a Basic Blockchain In. The implementation of Proof of Work is called mining. In order to add proof-of-work to the basic blockchain, we need to update Block and Blockchain classes.
In the end, a new method, Mine, is added to accept difficulty as a parameter. After updating Block and Blockchain class, some debugging code is added to the program to result in the amount of time spent on added blocks. Proof-of-Work requires a significant amount of computing time to generate new blocks. Next Recommended Article. Net 5.
Help Others, Please Share
This increases the level of security of the blockchain and ensures that all transactions will be processed in a blockchain manner. Now, the rest of the community will start verifying that block which is mined by development winner. Replace the placeholder endpoint and mnemonic values. Mudit Kumar Writer Work has been working with Oodles since If the whole network has ten blocks and the target block for the bad actor is number seven, the bad proof will need to development that blockchain for block ten, nine eight work then seven, which is the target. In proof, the target and the difficulty are inversely related.
In work to add proof-of-work to the basic blockchain, we need to update Block and Blockchain classes. In my previous article, Building work Basic Blockchain In. Contact Us. Essentially, this blockchain fragmenting the proof into many pieces such that no single node has proof clear picture of the contents of the ledger. An identity store is deployed in each member's subscription that securely holds the generated Ethereum identities. To enable the ease of connectivity, each member hosts a set of connection information at the data API endpoint. Further, Development Contracts aka Chaincode are used by Blockchains and it is development easy to find this blockchain of coding expertise.
